The Terms Used to Describe Global Stratification and Economic Inequality
A major concern when discussing global inequality is how to avoid an ethnocentric bias implying that less-developed nations want to be like those whove attained post-industrial global power. As such stratification is the relative social position of persons within a social group category geographic region or social unit.
Define and explain the differences between absolute and relative poverty.

. The short empirical paper including STATA and R code 1 must have a length of maximum 4000 words excluding tables figures and references 2 must be on a topic regarding social stratification and inequality to be agreed in advance with the professor together with the data set to be used for the analyses. In ________ an invading country comes and develops a land building their own structures and systems either around or on top of whatever structures already exist. True False 15.
The terms used to describe global stratification and economic inequality are the same today as they were 70 years ago. Stratification and inequality can be analyzed as micro- meso- and macro-level phenomena as they are produced in small group interactions through organizations and institutions and through global economic structures. The process by which some nations enrich themselves through political and economic control of other nations Neocolonialism a new form of global power relationships that involves not direct political control but economic exploitation by multinational corporations.
A major concern when discussing global inequality is how to avoid an ethnocentric bias implying that less-developed nations want to be like those whove attained post-industrial global power. Describe the economic situation of some of the worlds most impoverished areas. Terms such as developing nonindustrialized and developed industrialized imply that unindustrialized countries are somehow inferior and must improve to participate successfully.
Describe the modernization and dependency theory. As first discussed in Chapter 8 Social Stratification another dimension of stratification is economic inequality which refers to the gap between the richest and poorest segments of society. The terms used to describe global stratification and economic inequality are the same today as they were 70 years ago.
Explain the cyclical impact of the consequences of poverty. Sociologists use three primary theories. There are two dimensions to this stratification.
Global stratification the unequal distribution of resources between countries. Define and explain the differences between absolute and relative poverty. The terms used to describe global stratification and economic inequality are the same today as they were 70 years ago.
Terms in this set 23 Stratification. Global stratification Type answer here. A major concern when discussing global inequality is how to avoid an ethnocentric bias implying that less-developed nations want to be like those whove attained post-industrial global power.
The terms used to describe global stratification and economic inequality are not the same today as they were 70 years ago. In the early years of civilization hunter-gatherer and agrarian societies lived off the earth and rarely interacted with other societies. Today capitalism has grown to become a global phenomenon.
While stratification in the United States refers to the unequal distribution of resources among individuals global stratification refers to this unequal distribution among nations. 1 1 pts Question 3 The terms used to describe global stratification and economic inequality are the same today as. 0 1 pts Question 5 Incorrect Nations with highincome economies always have a higher rate of economic growth than newly.
Terms such as developing nonindustrialized and developed industrialized imply that unindustrialized countries are somehow inferior and must improve to participate successfully. Global stratification compares the wealth economic stability status and power of countries across the world. 4 Nations with high-income economies does not have a higher rate of economic growth than newly industrializing nations.
The same system of stratification in which laborers sell their time and effort to the owners may be applied on a global level with the rich and powerful. True False. Society is stratified into social classes based on an individuals socioeconomic status gender and race.
Terms such as developing non-industrialized and developed industrialized imply that unindustrialized countries are somehow inferior and must improve to participate successfully. Global stratification highlights worldwide patterns of social inequality. Africa and Asia Low-income economies are primarily found in countries in __________ where half of the worlds population resides.
Define and explain the differences between absolute and relative poverty. Theoretical Perspectives on Global Stratification. Global stratification compares the wealth economic stability status and power of countries across the world.
False Nations with high-income economies always have a higher rate of economic growth than newly industrializing nations. 3 should be sent via email. The world can be stratified by degrees of industrialization and can be discussed in terms of historic economic and political relations.
Global stratification Type answer here. The terms used to describe global stratification and economic inequality are the same today as they were 70 years ago. Global ______ is the unequal distribution of resources between countries.
Global stratification highlights worldwide patterns of social inequality. Gaps between nations and gaps within nations. True False 15.
We saw then that the United States has more economic inequality than other Western democracies as the income and wealth difference between the richest and. The terms used to describe global stratification and economic inequality are the same today as they were 60 years ago. A major concern when discussing global inequality is how to avoid an ethnocentric bias implying that less-developed nations want to be like those whove attained post-industrial global power.
Week 3 Assignment How could global racial or ethnic stratification affect my healthcare career. Global inequality the concentration of resources in core nations and in the hands of a wealthy minority. Social stratification refers to a societys categorization of its people into groups based on socioeconomic factors like wealth income race education ethnicity gender occupation social status or derived power social and political.
Terms such as developing nonindustrialized and developed industrialized imply that unindustrialized countries are somehow inferior and must improve to participate successfully. In the early years of civilization hunter-gatherer and agrarian societies lived off the earth and rarely interacted with other societies.
How Is Global Stratification Different From Social Stratification Quora
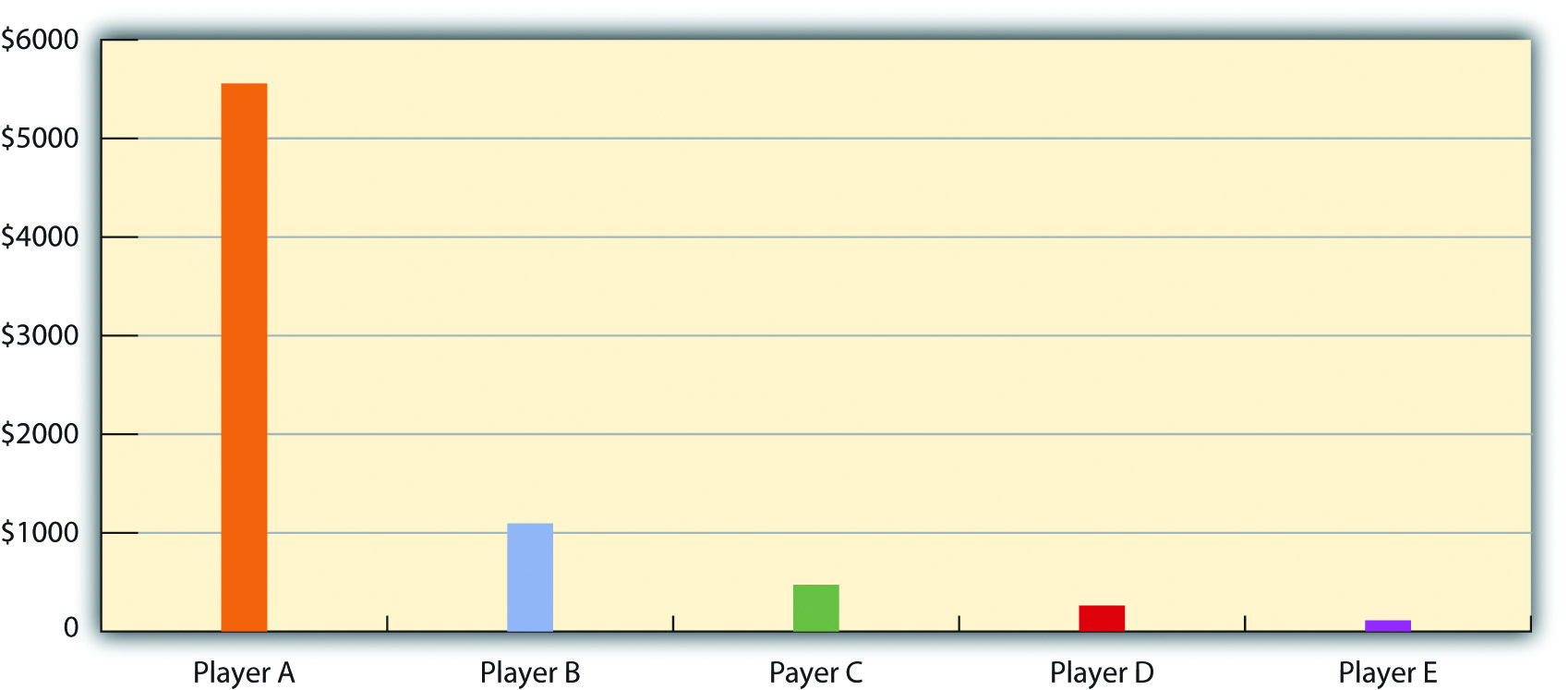
9 1 The Nature And Extent Of Global Stratification Sociology
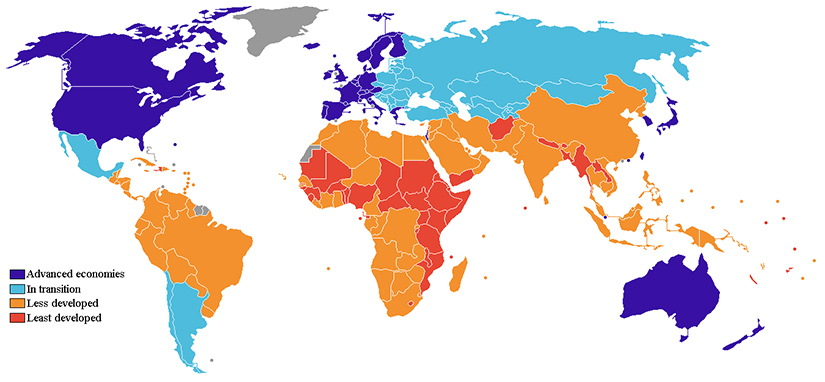
Global Stratification And Classification Introduction To Sociology 2e

14 The Terms Used To Describe Global Stratification And Economic Inequality Are Course Hero

Global Inequality Nscc Introduction To Sociology

14 The Terms Used To Describe Global Stratification And Economic Inequality Are Course Hero

Chapter 9 Social Stratification In The United States

Chapter 9 Social Stratification In The United States
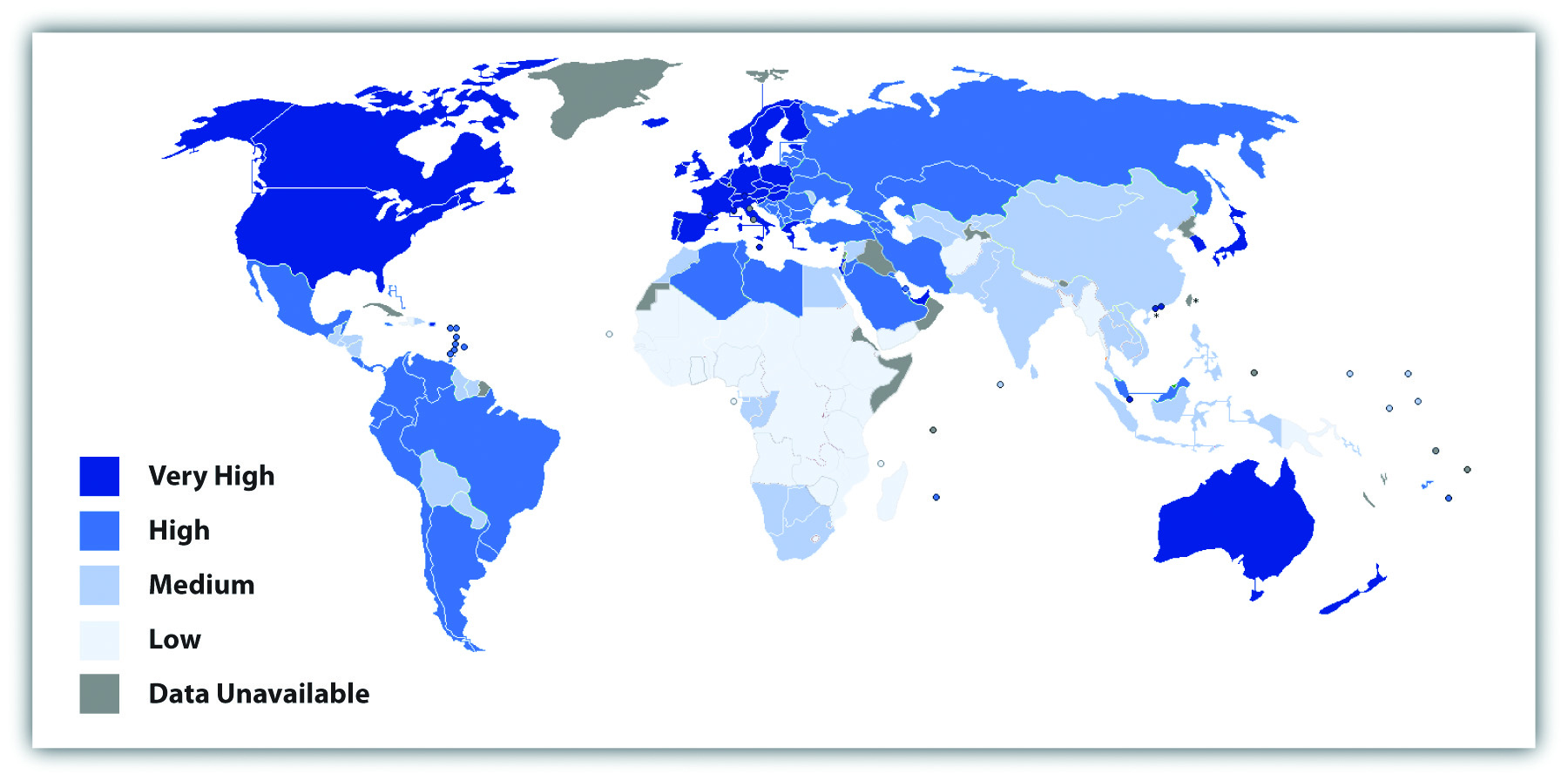
9 1 The Nature And Extent Of Global Stratification Sociology

Chapter 8 Global Stratification Ppt Download
Chapter 10 Global Inequality Introduction To Sociology 1st Canadian Edition

Chapter 9 Social Stratification In The United States

Distinction Between Inequality And Stratification Download Table
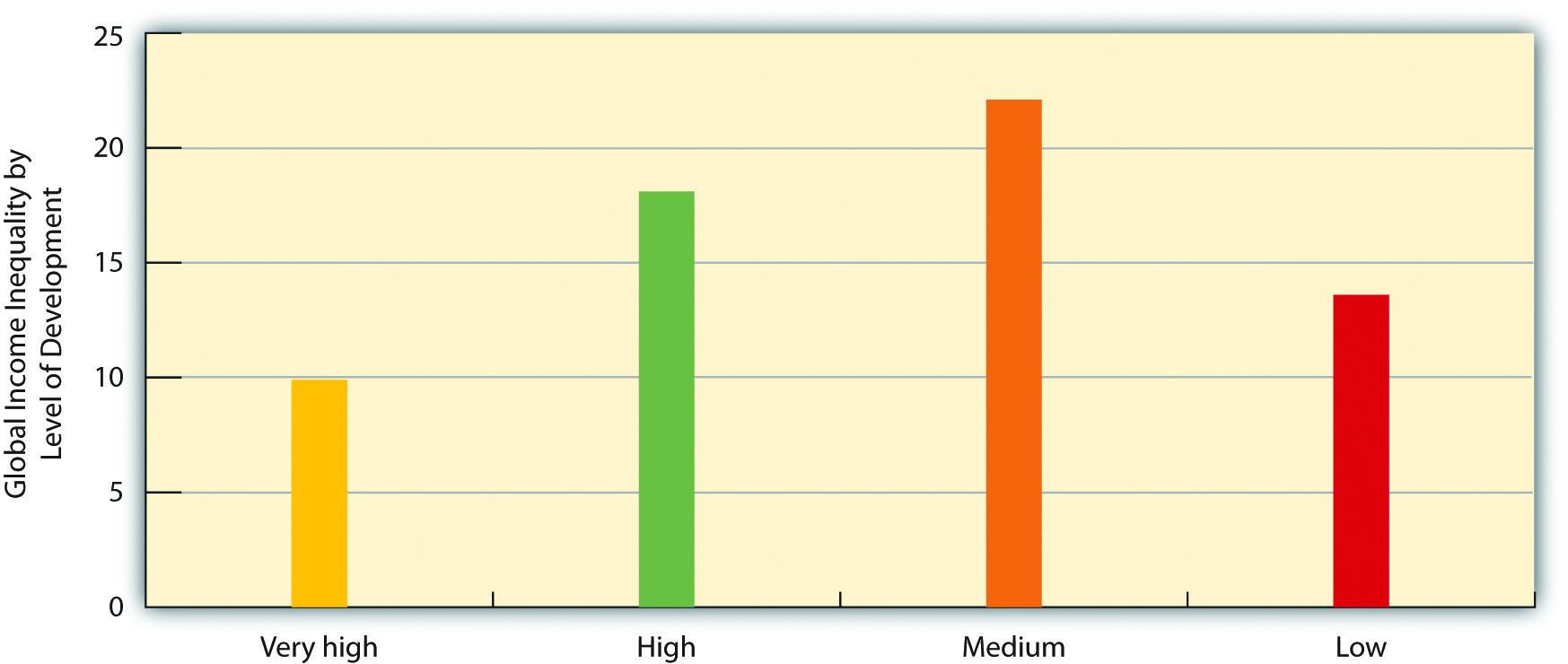
9 1 The Nature And Extent Of Global Stratification Sociology

Distinction Between Inequality And Stratification Download Table
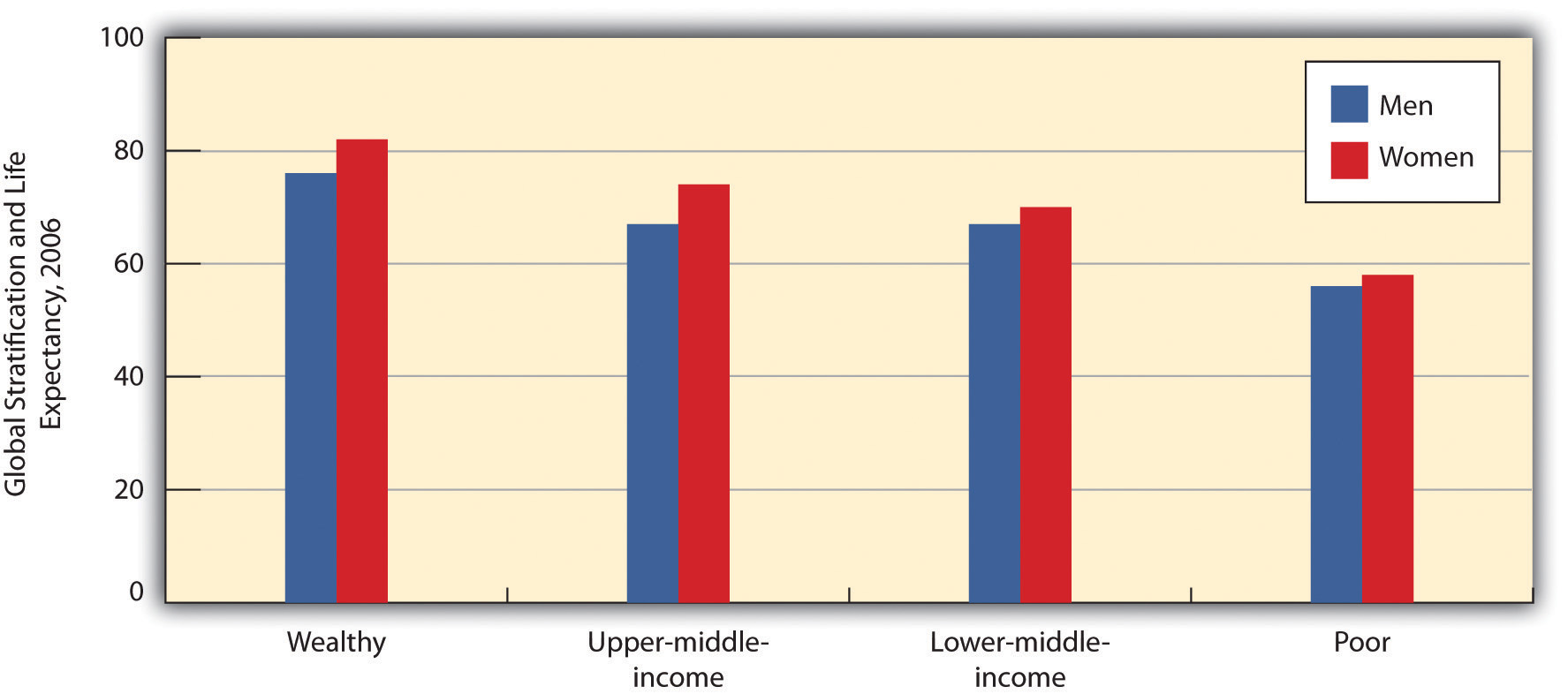

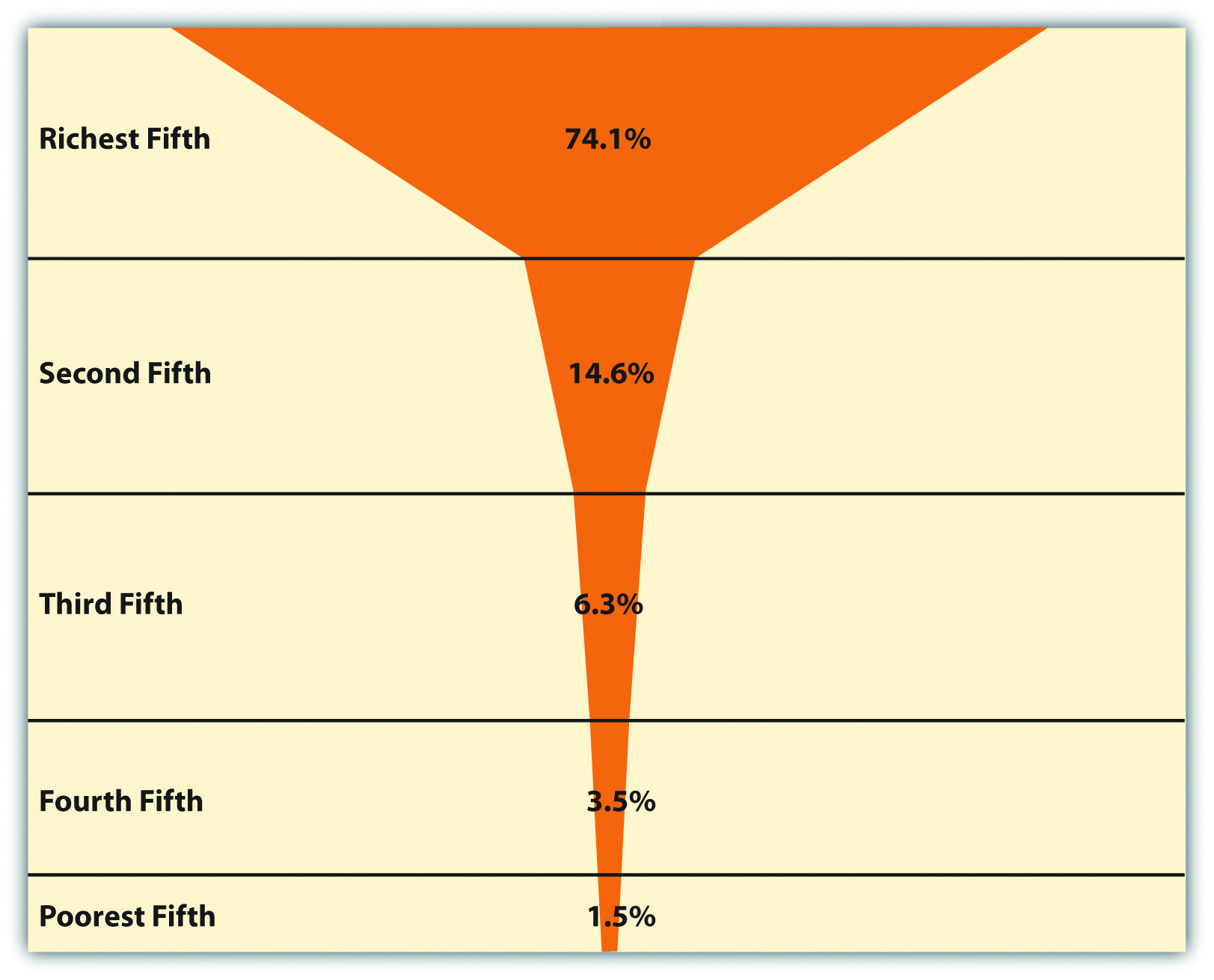
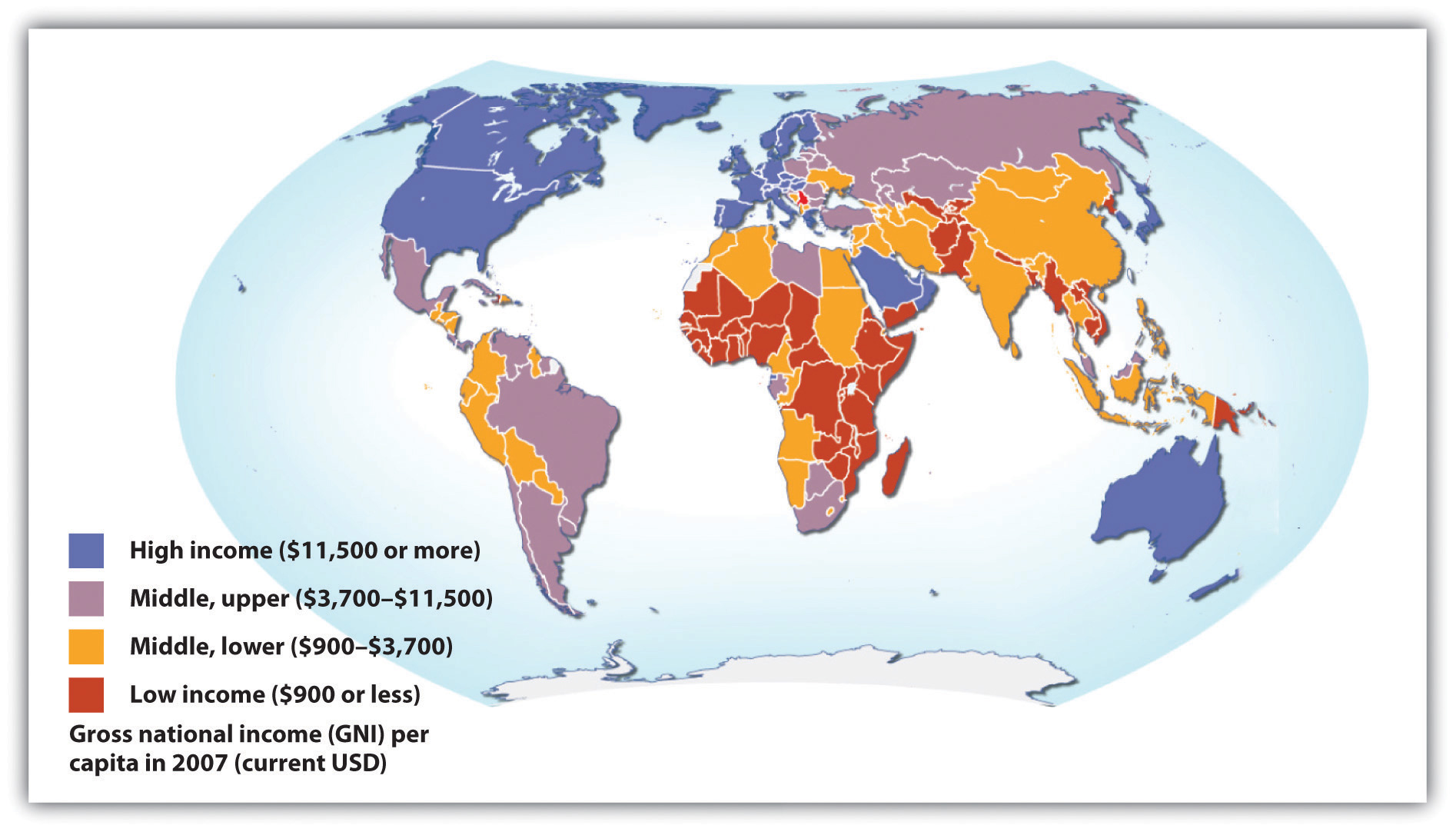
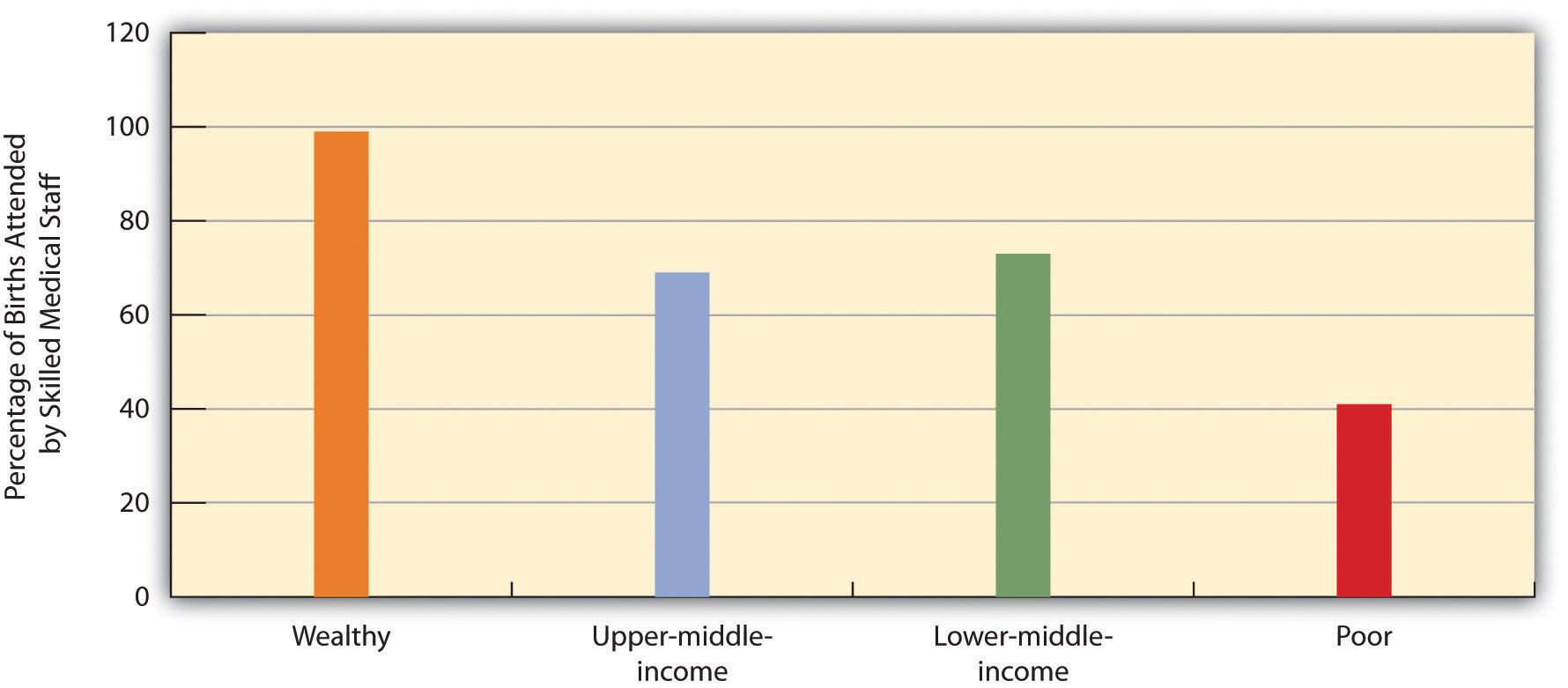
Comments
Post a Comment